python中的迭代器
2018-03-30 本文已影响0人
WillCheng
yield关键字
用法
普通函数:
>>> def f1(): return 'f1'
>>> f1()
'f1'
带有yield关键字的函数:
>>> def f2(): yield 'f2'
>>> f2()
<generator object f2 at 0x7f453255e4c0>
>>> next(f2())
'f2'
yield将函数的返回值变成了迭代器,其相当于获取函数运算结果的入口
next()为python的内置函数,用于从迭代器获取函数运算结果
机制
>>> def func():
... i = 0
... while True:
... yield i
... i += 1
...
>>> f = func()
>>> [next(f), next(f), next(f)]
[0, 1, 2]
相当于将函数“暂停”在yield处,再次调用next()则执行到下一个yield
用法举例
for...in
>>> def func():
... i = 0
... while i < 3:
... yield i
... i += 1
... raise StopIteration # 该行替换成return或者不写有同样的效果
...
>>> for i in func():
... print(i)
...
0
1
2
与range(n)相比省很大内存空间
内置send()函数
>>> def func():
... i = 0
... while True:
... i += yield i
...
>>> f = func()
>>> next(f)
0
>>> f.send(5)
5
>>> f.send(5)
10
>>> f.send(5)
15
send(X)调用将X作为上次执行到的yield表达式的值(此处相当于i += X),并再次执行next()。用于介入迭代过程
注意第一次执行next()后函数停止的位置,此时“+=”运算还未被执行:
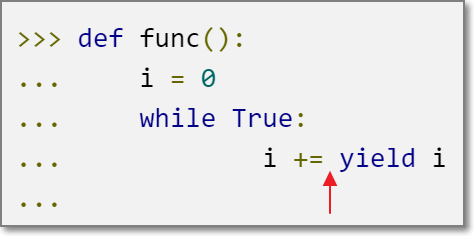 image.png-14kB
image.png-14kB
!!必须执行至少一次next()后才能执行send(),如下:
>>> f.send(5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: can't send non-None value to a just-started generator
类的_iter() 、_next()方法
除了包含yield的函数,还可以自己定义迭代器对象
内置函数iter(obj)调用相当于通过执行obj对象的_iter()方法获取迭代器对象
内置函数next(obj)调用相当于通过执行obj对象的_next()方法获取迭代结果
>>> class counter:
def __init__(self):
self.i = 0
def __iter__(self):
return self
def __next__(self):
self.i += 1
if self.i <= 3: return self.i
else: raise StopIteration
>>> f = iter(counter())
>>> print([next(f), next(f), next(f)])
[1, 2, 3]


