如何构建SNPs-based phylogenetic tree
如果根据SNP或者Indel 构建其系统进化树,可以展示群体中不同个体的相互关系,基因变异相似的往往会在同一个树的cluster中,一颗好的树可以给你一个群体大概的分类(你这个群体中有多少个cluster,一般同一个亚种或者有亲缘关系的个体会形成一个cluster),这是群体遗传中重要的一部分。其构建的核心原理就是把每个位点SNPs的信息提取,然后计算每个变异位点的差异得到算法中的“距离”。
在实战中,我们群体中样本的数量往往会是成百的,所以一般call出来的SNP变异的位点,或者说文件大小会很大,如果我们直接将没有过滤掉的文件拿来直接构建系统发育树,这不但会产生很大的误差(低质量的位点会影响距离的计算),而且一般的构树软件也不难接受如此大的文件,一来很消耗内存,二来运算量很大,你可能需要几个星期或几个月去完成你的建树。
这个时候你需要首先对你raw SNP calling的结果进行初步的过滤。
Filtering the raw SNPs vcf file
经典的过滤方式,,保留比较可信的变异位点
only include SNPs with MAF >= 0.05 and include only SNPs with a 90% genotyping rate (10% missing) use
~/biosoft/plink --vcf All_Gm_combine.vcf --maf 0.05 --geno 0.1 --recode vcf-iid --out All_test_11 --allow-extra-chr
进一步根据,.对标记进行中性LD筛选,并提取
用到的参数的基本介绍
--indep-pairphase [window size]<kb> [step size (variant ct)] [r^2 threshold]
~/biosoft/plink --vcf All_test_11.vcf --allow-extra-chr--indep-pairwise 50 10 0.2 --out test_12
~/biosoft/plink --allow-extra-chr --extract test_12.prune.in --make-bed --out test_12.prune.in --recode vcf-iid --vcf All_edit_Gm_tab.vcf
具体的建树过程我用了两种不同的工具和不同的算法进行构建
Methods 1 Megax
Mega是一款很经典的构树软件,重比对到建树,还有各种不同参数的选择都做的不错。而且它还支持各种平台有user interface的版本和命令行的版本,方便我们去使用。
工具下载地址:
首先将vcf 格式转成phylip格式
Transferrring the format into phylip
python2 vcf2phylip.py -i All_edit_Gm_tab.vcf
用到的 Script:
'''
The script converts a collection of SNPs in VCF format into a PHYLIP, FASTA,
NEXUS, or binary NEXUS file for phylogenetic analysis. The code is optimized
to process VCF files with sizes >1GB. For small VCF files the algorithm slows
down as the number of taxa increases (but is still fast).
'''
__author__ = "Edgardo M. Ortiz"
__credits__ = "Juan D. Palacio-Mejía"
__version__ = "1.5"
__email__ = "e.ortiz.v@gmail.com"
__date__ = "2018-04-24"
import sys
import os
import argparse
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Converts SNPs in VCF format into an alignment for phylogenetic analysis")
parser.add_argument("-i", "--input", action="store", dest="filename", required=True,
help="Name of the input VCF file")
parser.add_argument("-m", "--min-samples-locus", action="store", dest="min_samples_locus", type=int, default=4,
help="Minimum of samples required to be present at a locus, default=4 since is the minimum for phylogenetics.")
parser.add_argument("-o", "--outgroup", action="store", dest="outgroup", default="",
help="Name of the outgroup in the matrix. Sequence will be written as first taxon in the alignment.")
parser.add_argument("-p", "--phylip-disable", action="store_true", dest="phylipdisable", default=False,
help="A PHYLIP matrix is written by default unless you enable this flag")
parser.add_argument("-f", "--fasta", action="store_true", dest="fasta", default=False,
help="Write a FASTA matrix, disabled by default")
parser.add_argument("-n", "--nexus", action="store_true", dest="nexus", default=False,
help="Write a NEXUS matrix, disabled by default")
parser.add_argument("-b", "--nexus-binary", action="store_true", dest="nexusbin", default=False,
help="Write a binary NEXUS matrix for analysis of biallelic SNPs in SNAPP, disabled by default")
args = parser.parse_args()
filename = args.filename
min_samples_locus = args.min_samples_locus
outgroup = args.outgroup
phylipdisable = args.phylipdisable
fasta = args.fasta
nexus = args.nexus
nexusbin = args.nexusbin
# Dictionary of IUPAC ambiguities for nucleotides
# '*' means deletion for GATK (and other software?)
# Deletions are ignored when making the consensus
amb = {("A","A"):"A",
("A","C"):"M",
("A","G"):"R",
("A","N"):"A",
("A","T"):"W",
("C","A"):"M",
("C","C"):"C",
("C","G"):"S",
("C","N"):"C",
("C","T"):"Y",
("G","A"):"R",
("G","C"):"S",
("G","G"):"G",
("G","N"):"G",
("G","T"):"K",
("N","A"):"A",
("N","C"):"C",
("N","G"):"G",
("N","N"):"N",
("N","T"):"T",
("T","A"):"W",
("T","C"):"Y",
("T","G"):"K",
("T","N"):"T",
("T","T"):"T",
("*","*"):"-",
("A","*"):"A",
("*","A"):"A",
("C","*"):"C",
("*","C"):"C",
("G","*"):"G",
("*","G"):"G",
("T","*"):"T",
("*","T"):"T",
("N","*"):"N",
("*","N"):"N"}
# Dictionary for translating biallelic SNPs into SNAPP
# 0 is homozygous reference
# 1 is heterozygous
# 2 is homozygous alternative
gen_bin = {"./.":"?",
".|.":"?",
"0/0":"0",
"0|0":"0",
"0/1":"1",
"0|1":"1",
"1/0":"1",
"1|0":"1",
"1/1":"2",
"1|1":"2"}
# Process header of VCF file
with open(filename) as vcf:
# Create a list to store sample names
sample_names = []
# Keep track of longest sequence name for padding with spaces in the output file
len_longest_name = 0
# Look for the line in the VCF header with the sample names
for line in vcf:
if line.startswith("#CHROM"):
# Split line into fields
broken = line.strip("\n").split("\t")
# If the minimum-samples-per-locus parameter is larger than the number of
# species in the alignment make it the same as the number of species
if min_samples_locus > len(broken[9:]):
min_samples_locus = len(broken[9:])
# Create a list of sample names and the keep track of the longest name length
for i in range(9, len(broken)):
name_sample = broken[i].replace("./","") # GATK adds "./" to sample names
sample_names.append(name_sample)
len_longest_name = max(len_longest_name, len(name_sample))
break
vcf.close()
# Output filename will be the same as input file, indicating the minimum of samples specified
outfile = filename.replace(".vcf",".min"+str(min_samples_locus))
# We need to create an intermediate file to hold the sequence data
# vertically and then transpose it to create the matrices
if fasta or nexus or not phylipdisable:
temporal = open(outfile+".tmp", "w")
# if binary NEXUS is selected also create a separate temporal
if nexusbin:
temporalbin = open(outfile+".bin.tmp", "w")
##################
# PROCESS VCF FILE
index_last_sample = len(sample_names)+9
# Start processing SNPs of VCF file
with open(filename) as vcf:
# Initialize line counter
snp_num = 0
snp_accepted = 0
snp_shallow = 0
snp_multinuc = 0
snp_biallelic = 0
while True:
# Load large chunks of file into memory
vcf_chunk = vcf.readlines(100000)
if not vcf_chunk:
break
# Now process the SNPs one by one
for line in vcf_chunk:
if not line.startswith("#") and line.strip("\n") != "": # pyrad sometimes produces an empty line after the #CHROM line
# Split line into columns
broken = line.strip("\n").split("\t")
for g in range(9,len(broken)):
if broken[g] in [".", ".|."]:
broken[g] = "./."
# Keep track of number of genotypes processed
snp_num += 1
# Print progress every 500000 lines
if snp_num % 500000 == 0:
print str(snp_num)+" genotypes processed"
# Check if the SNP has the minimum of samples required
if (len(broken[9:]) - ''.join(broken[9:]).count("./.")) >= min_samples_locus:
# Check that ref genotype is a single nucleotide and alternative genotypes are single nucleotides
if len(broken[3]) == 1 and (len(broken[4])-broken[4].count(",")) == (broken[4].count(",")+1):
# Add to running sum of accepted SNPs
snp_accepted += 1
# If nucleotide matrices are requested
if fasta or nexus or not phylipdisable:
# Create a dictionary for genotype to nucleotide translation
# each SNP may code the nucleotides in a different manner
nuc = {str(0):broken[3], ".":"N"}
for n in range(len(broken[4].split(","))):
nuc[str(n+1)] = broken[4].split(",")[n]
# Translate genotypes into nucleotides and the obtain the IUPAC ambiguity
# for heterozygous SNPs, and append to DNA sequence of each sample
site_tmp = ''.join([(amb[(nuc[broken[i][0]], nuc[broken[i][1]])]) for i in range(9, index_last_sample)])
# Write entire row of single nucleotide genotypes to temporary file
temporal.write(site_tmp+"\n")
# Write binary NEXUS for SNAPP if requested
if nexusbin:
# Check taht the SNP only has two alleles
if len(broken[4]) == 1:
# Add to running sum of biallelic SNPs
snp_biallelic += 1
# Translate genotype into 0 for homozygous ref, 1 for heterozygous, and 2 for homozygous alt
binsite_tmp = ''.join([(gen_bin[broken[i][0:3]]) for i in range(9, index_last_sample)])
# Write entire row to temporary file
temporalbin.write(binsite_tmp+"\n")
else:
# Keep track of loci rejected due to multinucleotide genotypes
snp_multinuc += 1
# Keep track of loci rejected due to exceeded missing data
snp_shallow += 1
else:
# Keep track of loci rejected due to exceeded missing data
snp_shallow += 1
# Print useful information about filtering of SNPs
print str(snp_num) + " genotypes processed in total"
print "\n"
print str(snp_shallow) + " genotypes were excluded because they exceeded the amount of missing data allowed"
print str(snp_multinuc) + " genotypes passed missing data filter but were excluded for not being SNPs"
print str(snp_accepted) + " SNPs passed the filters"
if nexusbin:
print str(snp_biallelic) + " SNPs were biallelic and selected for binary NEXUS"
print "\n"
vcf.close()
if fasta or nexus or not phylipdisable:
temporal.close()
if nexusbin:
temporalbin.close()
#######################
# WRITE OUTPUT MATRICES
if not phylipdisable:
output_phy = open(outfile+".phy", "w")
header_phy = str(len(sample_names))+" "+str(snp_accepted)+"\n"
output_phy.write(header_phy)
if fasta:
output_fas = open(outfile+".fasta", "w")
if nexus:
output_nex = open(outfile+".nexus", "w")
header_nex = "#NEXUS\n\nBEGIN DATA;\n\tDIMENSIONS NTAX=" + str(len(sample_names)) + " NCHAR=" + str(snp_accepted) + ";\n\tFORMAT DATATYPE=DNA" + " MISSING=N" + " GAP=- ;\nMATRIX\n"
output_nex.write(header_nex)
if nexusbin:
output_nexbin = open(outfile+".bin.nexus", "w")
header_nexbin = "#NEXUS\n\nBEGIN DATA;\n\tDIMENSIONS NTAX=" + str(len(sample_names)) + " NCHAR=" + str(snp_biallelic) + ";\n\tFORMAT DATATYPE=SNP" + " MISSING=?" + " GAP=- ;\nMATRIX\n"
output_nexbin.write(header_nexbin)
# Store index of outgroup in list of sample names
idx_outgroup = "NA"
# Write outgroup as first sequence in alignment if the name is specified
if outgroup in sample_names:
idx_outgroup = sample_names.index(outgroup)
if fasta or nexus or not phylipdisable:
with open(outfile+".tmp") as tmp_seq:
seqout = ""
# This is where the transposing happens
for line in tmp_seq:
seqout += line[idx_outgroup]
# Write FASTA line
if fasta:
output_fas.write(">"+sample_names[idx_outgroup]+"\n"+seqout+"\n")
# Pad sequences names and write PHYLIP or NEXUS lines
padding = (len_longest_name + 3 - len(sample_names[idx_outgroup])) * " "
if not phylipdisable:
output_phy.write(sample_names[idx_outgroup]+padding+seqout+"\n")
if nexus:
output_nex.write(sample_names[idx_outgroup]+padding+seqout+"\n")
# Print current progress
print "Outgroup, "+outgroup+", added to the matrix(ces)."
if nexusbin:
with open(outfile+".bin.tmp") as bin_tmp_seq:
seqout = ""
# This is where the transposing happens
for line in bin_tmp_seq:
seqout += line[idx_outgroup]
# Write line of binary SNPs to NEXUS
padding = (len_longest_name + 3 - len(sample_names[idx_outgroup])) * " "
output_nexbin.write(sample_names[idx_outgroup]+padding+seqout+"\n")
# Print current progress
print "Outgroup, "+outgroup+", added to the binary matrix."
# Write sequences of the ingroup
for s in range(0, len(sample_names)):
if s != idx_outgroup:
if fasta or nexus or not phylipdisable:
with open(outfile+".tmp") as tmp_seq:
seqout = ""
# This is where the transposing happens
for line in tmp_seq:
seqout += line[s]
# Write FASTA line
if fasta:
output_fas.write(">"+sample_names[s]+"\n"+seqout+"\n")
# Pad sequences names and write PHYLIP or NEXUS lines
padding = (len_longest_name + 3 - len(sample_names[s])) * " "
if not phylipdisable:
output_phy.write(sample_names[s]+padding+seqout+"\n")
if nexus:
output_nex.write(sample_names[s]+padding+seqout+"\n")
# Print current progress
print "Sample "+str(s+1)+" of "+str(len(sample_names))+", "+sample_names[s]+", added to the nucleotide matrix(ces)."
if nexusbin:
with open(outfile+".bin.tmp") as bin_tmp_seq:
seqout = ""
# This is where the transposing happens
for line in bin_tmp_seq:
seqout += line[s]
# Write line of binary SNPs to NEXUS
padding = (len_longest_name + 3 - len(sample_names[s])) * " "
output_nexbin.write(sample_names[s]+padding+seqout+"\n")
# Print current progress
print "Sample "+str(s+1)+" of "+str(len(sample_names))+", "+sample_names[s]+", added to the binary matrix."
if not phylipdisable:
output_phy.close()
if fasta:
output_fas.close()
if nexus:
output_nex.write(";\nEND;\n")
output_nex.close()
if nexusbin:
output_nexbin.write(";\nEND;\n")
output_nexbin.close()
if fasta or nexus or not phylipdisable:
os.remove(outfile+".tmp")
if nexusbin:
os.remove(outfile+".bin.tmp")
print "\nDone!\n"
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
然后使用megax的内置工具将phylip格式的文件转化成mega格式的文件
 1.PNG-24.7kB
1.PNG-24.7kB
使用MEGAX常用的参数去构建系统进化树,因为我的样本都是来自同一个specie的不同亚种,所以NJ tree 已经适用了。
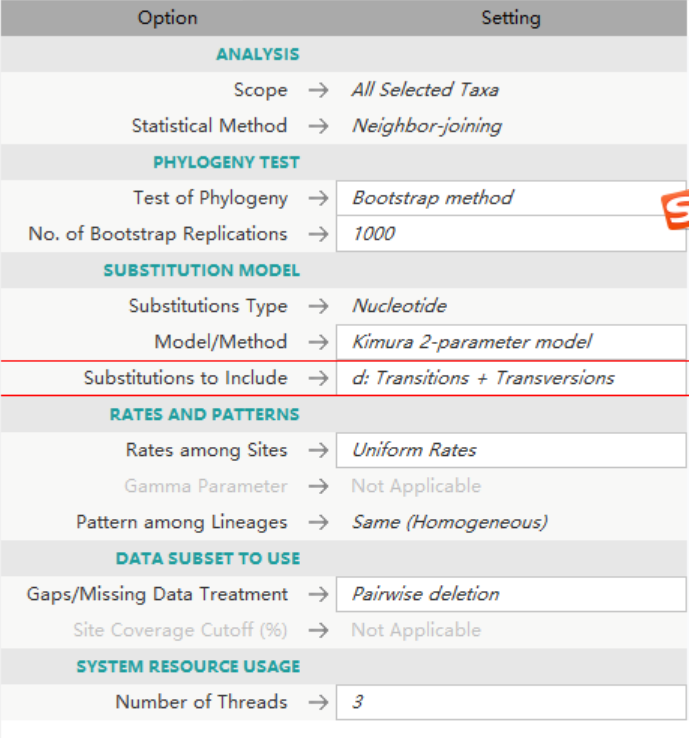 捕获.PNG-163.8kB
捕获.PNG-163.8kB
最后生成.nwk 文件,进一步使用其他工具将其美化。
Method 2 SnPhylop
然后除了Mega之外SNPhylo这款工具也很适合利用具有很多个个体的变异文件来构建系统进化树。这款软件有其内置的过滤机制,可以根据你所选参数的条件进行过滤(或者其default的参数),然后最后还会帮你把图也输出(当然不太美观,最好还是要进行后期的美化)。它的画图需要用到R包,这里如果你想要它帮你画图,它所需要的R包也要装好。
下载地址
http://chibba.pgml.uga.edu/snphylo/
其算法及流程

用法manual:
Usage:
snphylo.sh -v VCF_file [-p Maximum_PLCS (5)] [-c Minimum_depth_of_coverage (5)]|-H HapMap_file [-p Maximum_PNSS (5)]|-s Simple_SNP_file [-p Maximum_PNSS (5)]|-d GDS_file [-l LD_threshold (0.1)] [-m MAF_threshold (0.1)] [-M Missing_rate (0.1)] [-o Outgroup_sample_name] [-P Prefix_of_output_files (snphylo.output)] [-b [-B The_number_of_bootstrap_samples (100)]] [-a The_number_of_the_last_autosome (22)] [-r] [-A] [-h]
Options:
-A: Perform multiple alignment by MUSCLE
-b: Performs (non-parametric) bootstrap analysis and generate a tree
-h: Show help and exit
-r: Skip the step removing low quality data (-p and -c option are ignored)
Acronyms:
PLCS: The percent of Low Coverage Sample
PNSS: The percent of Sample which has no SNP information
LD: Linkage Disequilibrium
MAF: Minor Allele Frequency
Simple SNP File Format:
#Chrom Pos SampleID1 SampleID2 SampleID3 ...
1 1000 A A T ...
1 1002 G C G ...
...
2 2000 G C G ...
2 2002 A A T ...
当安装好工具,准确放好输入文件,简单敲一行命令,运算就会开始了:
~/biosoft/SNPhylo/snphylo.sh -v Gpan.prune.in.vcf -A -b -B 300
运算完,生成的文件如下
rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 98K Sep 4 09:08 snphylo.output.bs.png
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 27K Sep 4 09:08 snphylo.output.bs.tree
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 4.9M Sep 1 20:04 snphylo.output.fasta
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 488M Sep 1 19:48 snphylo.output.filtered.vcf
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 31M Sep 1 20:03 snphylo.output.gds
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 72K Sep 1 20:03 snphylo.output.id.txt
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 95K Sep 3 19:37 snphylo.output.ml.png
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 25K Sep 3 19:37 snphylo.output.ml.tree
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 257K Sep 3 19:37 snphylo.output.ml.txt
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 5.4M Sep 1 20:49 snphylo.output.phylip.txt
-rw-r----- 1 21230309 domain users 20K Sep 1 19:16 snphylo.tar.gz


