【翻译】RAML1.0规范: RESTful API模型语言(2
RAML数据类型
引言
RAML 1.0引入了数据类型的概念,它提供了一种简洁而强大的方式来描述API中的数据。数据类型添加用于根据类型声明验证数据的规则。有效数据遵守类型的所有规则。数据类型可以描述基本或资源URI参数,查询参数,请求或响应头或请求或响应体。数据类型是内置或自定义的。内置类型可以在API期望数据的任何地方使用。自定义类型可以通过扩展内置类型以及命名和使用像内置类型来定义。扩展类型不能创建任何循环依赖。类型可以内联扩展。
以下RAML示例定义了包含firstname,lastname和age属性的类型声明的用户类型。该示例将属性声明为内置类型字符串和数字。稍后,用户类型用于描述有效载荷的类型(模式)。
#%RAML 1.0
title: API with Types
types:
User:
type: object
properties:
firstname: string
lastname: string
age: number
/users/{id}:
get:
responses:
200:
body:
application/json:
type: User
RAML类型声明类似于JSON模式定义。实际上,可以使用RAML类型而不是JSON和XML模式,或者与它们共存。然而,RAML类型语法被设计为比JSON和XML模式更容易和更简洁,同时保持它们的灵活性和表达性。以下代码段显示了一些类型声明的示例:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API with Types
mediaType: application/json
types:
Org:
type: object
properties:
onCall: AlertableAdmin
Head: Manager
Person:
type: object
properties:
firstname: string
lastname: string
title?: string
Phone:
type: string
pattern: "[0-9|-]+"
Manager:
type: Person
properties:
reports: Person[]
phone: Phone
Admin:
type: Person
properties:
clearanceLevel:
enum: [ low, high ]
AlertableAdmin:
type: Admin
properties:
phone: Phone
Alertable: Manager | AlertableAdmin
/orgs/{orgId}:
get:
responses:
200:
body:
application/json:
type: Org
概述
本节内容丰富。
RAML类型系统从面向对象的编程语言(如Java)以及XSD和JSON模式中借用。
RAML类型概述:
- 类型类似于Java类。
- 类型从JSON Schema,XSD和更具表达性的面向对象语言借用附加功能。
- 您可以定义从其他类型继承的类型。
- 允许多重继承。
- 类型分为四个族:外部,对象,数组和标量。
- 类型可以定义两种类型的成员:属性和切面。两者都是继承的。
- 属性是常规的,面向对象的属性。
-
切面是特殊的 配置。您可以根据切面值的特性对类型进行特殊化处理。
示例:minLength,maxLength
- 只有对象类型可以声明属性。所有类型都可以声明切面。
定义类型
类型可以在API期望数据的内部声明,在API根目录的可选类型节点中或在包含的库中声明。要声明一个类型,你使用一个映射,其中key表示类型的名称,它的值是一个类型声明。
types:
Person: # key name
# value is a type declaration
类型声明
类型声明引用另一个类型,或者通过添加功能面(例如属性)或非功能面(例如描述)来包装或扩展另一个类型,或者是使用其他类型的类型表达式。这里是所有类型声明可以有的方面;某些类型声明可能有其他方面:
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| default? | 类型的默认值。当API请求完全丢失某个类型的实例时,例如,当某个类型描述的查询参数从请求中完全丢失时,API必须表现为API客户端已向该实例发送了该类型的实例value是默认切面中的值。类似地,当API响应完全丢失类型的实例时,客户端必须表现为API服务器已返回该类型的实例,实例值是默认切面中的值。一个特殊的情况是URI参数:对于这些,如果没有给出URI参数的实例,客户端必须替换默认切面中的值。 |
| schema? | 等效“types”切面的别名,以与RAML 0.8兼容。已弃用 - API定义应使用“type”切面,因为该切面名称的“schema”别名可能会在未来的RAML版本中删除。 “type”构面支持XML和JSON模式。 |
| type? | 当前类型扩展或只是包装的类型。类型节点的值必须是 a)用户定义类型的名称或 b)内置RAML数据类型(对象,数组或标量类型之一)的名称,或 c)内联类型声明。 |
| example? | 这种类型的实例的示例,其可以例如通过文档生成器用于为这种类型的对象生成样本值。当“examples”切面已经定义时,“example”切面必须不可用。有关详细信息,请参阅示例部分。 |
| examples? | 这种类型的实例的示例,其可以例如通过文档生成器用于为这种类型的对象生成样本值。当“examples”切面已经定义时,“example”切面必须不可用。有关详细信息,请参阅示例部分。 |
| displayName? | 类型的替代,人性化的名称 |
| description? | 一个实质的,人性化的描述类型。它的值是一个字符串,可以使用markdown格式化。 |
| (<注释名称>)? | 要应用于此API的注释。注释是具有以“(”和“”)结尾的键的映射,其中括号中的文本是注释名称,值是该注释的实例。 |
| facets? | 将由任何扩展子类型继承和应用的其他用户定义限制的映射。有关详细信息,请参阅用户定义的切面。 |
| xml? | 配置此类型实例的XML序列化的功能。 |
| enum? | 此类型的实例的所有可能值的枚举。该值是一个包含这些可能值的表示的数组;此类型的实例必须等于这些值之一。 |
“schema”和“type”切面是相互排斥和同义的:处理器不得允许在同一类型声明内明确或隐含地指定这两者。因此,以下示例无效:
types:
Person:
schema: # invalid as mutually exclusive with `type`
type: # invalid as mutually exclusive with `schema`
/resource:
get:
responses:
200:
body:
application/json: # start type declaration
schema: # invalid as mutually exclusive with `type`
type: # invalid as mutually exclusive with `schema`
我们建议使用“type”构面而不是“schema”,因为模式别名已过时,可能会在将来的RAML版本中删除。此外,“type”构面支持XML和JSON模式。
内置类型
RAML类型系统定义了以下内置类型:
除了内置类型,RAML类型系统还允许定义JSON或XML模式.
下图显示了继承树,从根级别开始,使用any。
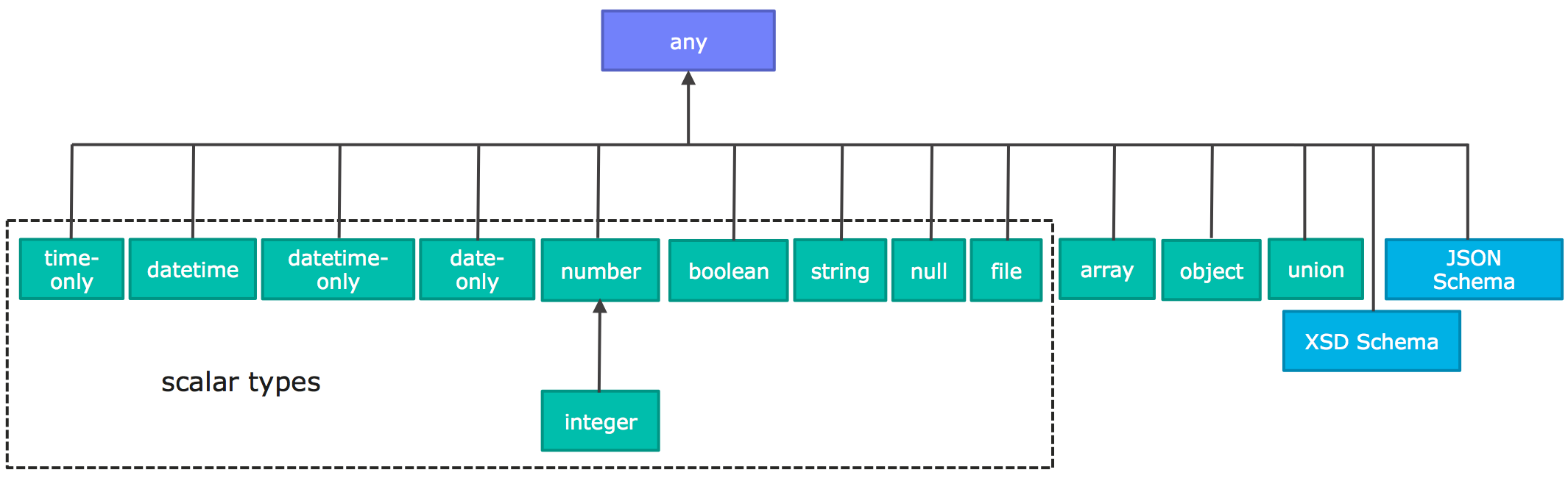 Types Hierarchy
Types Hierarchy
任意类型
每个类型,无论是内置的还是用户定义的,在它的继承树的根处都有any类型。根据定义,any类型是一种不施加任何限制的类型,即任何数据实例对其有效。
任何类型的“基本”类型是其继承树中的类型,它直接在根处扩展any类型;因此,例如,如果一个自定义类型status扩展了内置类型integer',它扩展了扩展any类型的内置类型integer,那么status的基本类型是number。请注意,类型可能有多个基本类型。
any类型没有切面。
对象类型
在其继承树中具有内置对象基类型的所有类型都可以在其类型声明中使用以下切面:
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| properties? | 这种类型的实例可以或必须具有的属性。 |
| minProperties? | 允许此类型实例的最小属性数。 |
| maxProperties? | 此类型实例允许的最大属性数。 |
| additionalProperties? | 一个布尔值,指示对象实例是否具有其他属性. Default: true
|
| discriminator? | 在运行时确定单个对象的具体类型,例如,当有效内容由于联合或继承而包含模糊类型时。该值必须与类型的一个声明的properties的名称匹配。不支持的实践是内联类型声明并使用具有非标量属性的discriminator。 |
| discriminatorValue? | 标识声明类型。需要在类型声明中包含一个“discriminator”切面。有效值是可以标识单个对象的类型并且在类型的层次结构中是唯一的实际值。不支持行内类型声明。 Default: 类型的名称 |
对象类型是通过从内置类型对象的显式继承创建的:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Person:
type: object
properties:
name:
required: true
type: string
属性声明
对象类型的属性使用可选的properties 切面定义。 RAML规范将“属性”漆面的值调用为“属性声明”。属性声明是键和值的映射。键是用于声明类型实例的有效属性名。这些值是类型的名称或内联类型声明。
属性声明可以指定属性是必需的还是可选的。
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| required? | 指定属性是否必需。<br /><br />Default: true. |
以下示例声明具有两个属性的对象类型:
types:
Person:
properties:
name:
required: true
type: string
age:
required: false
type: number
以下示例显示了一个常用的惯用法:
types:
Person:
properties:
name: string # equivalent to ->
# name:
# type: string
age?: number # optional property; equivalent to ->
# age:
# type: number
# required: false
当一个属性上的required切面在类型声明中被明确指定时,其属性名中的任何问号都被视为属性名的一部分,而不是该属性是可选的。
例如,
types:
profile:
properties:
preference?:
required: true
profile类型有一个名为preference?的属性,它包含了尾随的问号。以下代码片段显示了两种preference选项的方法:
types:
profile:
properties:
preference?:
required: false
或
types:
profile:
properties:
preference??:
注意:
当对象类型不包含“属性”切面时,假定该对象是不受约束的,因此能够包含任何类型的任何属性。
其他属性
默认情况下,对象的任何实例都可以具有除其数据类型property切面中指定的属性之外的其他属性。假设以下代码是上一节中描述的数据类型“Person”的实例。
Person:
name: "John"
age: 35
note: "US" # valid additional property `note`
属性note没有在Person数据类型中显式声明,但是有效,因为默认情况下所有其他属性都有效。
要限制属性的添加,可以将additionalProperties facet的值设置为false,也可以指定与键集合匹配的正则表达式模式并限制其值。后者称为“模式属性”。模式由一对开头和结尾的/字符描述,如下所示:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Person:
properties:
name:
required: true
type: string
age:
required: false
type: number
/^note\d+$/: # restrict any properties whose keys start with "note"
# followed by a string of one or more digits
type: string
此模式属性限制键的开头为“note”,后跟一个或多个数字的字符串的任何其他属性。因此,声明一个附加的note属性值为“US”的对象实例的示例是有效的,但是相同的属性对非字符串值无效:
Person:
name: "John"
age: 35
note: 123 # not valid as it is not a string
address: "US" # valid as it does not match the pattern
要强制所有其他属性为字符串,不管它们的键,请使用:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Person:
properties:
name:
required: true
type: string
age:
required: false
type: number
//: # force all additional properties to be a string
type: string
如果模式属性正则表达式也匹配显式声明的属性,则明确声明的属性定义优先。如果两个或多个模式属性正则表达式匹配数据类型的实例中的属性名称,则以第一个为准。
此外,如果在给定的类型定义中additionalProperties是false(显式地或通过继承),则不允许在该定义中显式地设置模式属性。如果givenProperties在给定的类型定义中为true(或省略),则允许模式属性,并进一步限制该类型允许的其他属性。
对象类型特殊化
您可以声明从其他对象类型继承的对象类型。子类型继承其父类型的所有属性。在以下示例中,类型“Employee”继承其父类型“Person”的所有属性。
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Person:
type: object
properties:
name:
type: string
Employee:
type: Person
properties:
id:
type: string
子类型可以覆盖其父类型的属性,具有以下限制:1)父类型中的必需属性不能在子类型中更改为可选,以及2)父类型中定义的属性的类型声明只能在子类型中更改为较窄类型(父类型的特殊化)。
使用鉴别器
当有效载荷由于联合或继承而包含模糊类型时,通常不可能在运行时区分单个对象的具体类型。例如,当将有效负载反序列化为静态类型语言时,可能发生此问题。
RAML处理器可以提供从一组可能类型中自动选择具体类型的实现,但是更简单的替换是存储与对象内部类型相关联的一些唯一值。
您使用discriminator切面设置对象属性的名称。对象属性的名称用于区分具体类型。 discriminatorValue存储可以标识单个对象的类型的实际值。默认情况下,discriminatorValue的值是类型的名称。
这里有一个例子说明如何使用discriminator:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Person:
type: object
discriminator: kind # refers to the `kind` property of object `Person`
properties:
kind: string # contains name of the kind of a `Person` instance
name: string
Employee: # kind can equal `Employee`; default value for `discriminatorValue`
type: Person
properties:
employeeId: integer
User: # kind can equal `User`; default value for `discriminatorValue`
type: Person
properties:
userId: integer
data:
- name: A User
userId: 111
kind: User
- name: An Employee
employeeId: 222
kind: Employee
您还可以为每个单独的具体类覆盖discriminatorValue的默认值。以下示例将使用小写的初始大写替换discriminatorValue的默认值:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Person:
type: object
discriminator: kind
properties:
name: string
kind: string
Employee:
type: Person
discriminatorValue: employee # override default
properties:
employeeId: string
User:
type: Person
discriminatorValue: user # override default
properties:
userId: string
data:
- name: A User
userId: 111
kind: user
- name: An Employee
employeeId: 222
kind: employee
对于任何内联类型声明或联合类型,都不能定义discriminator或discriminatorValue。
# valid whenever there is a key name that can identify a type
types:
Device:
discriminator: kind
properties:
kind: string
# invalid in any inline type declaration
application/json:
discriminator: kind
properties:
kind: string
# invalid for union types
PersonOrDog:
type: Person | Dog
discriminator: hasTail
数组类型
数组类型通过类型表达式末尾的数组限定符[]或使用array作为type切面的值来声明。如果要定义顶级数组类型,例如下面示例中的Emails,你可以声明以下前面描述的那些切面,以进一步限制数组类型的行为。
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| uniqueItems? | 布尔值,指示数组中的项是否必须是唯一的。 |
| items? | 指示数组中所有项目继承的类型。可以是对现有类型或内联类型声明的引用. |
| minItems? | 数组中的最小项数。值必须等于或大于0。<br /><br />Default: 0. |
| maxItems? | 数组中的最大项数。值必须等于或大于0。<br /><br />Default: 2147483647. |
以下两个示例都有效:
types:
Email:
type: object
properties:
subject: string
body: string
Emails:
type: Email[]
minItems: 1
uniqueItems: true
example: # example that contains array
- # start item 1
subject: My Email 1
body: This is the text for email 1.
- # start item 2
subject: My Email 2
body: This is the text for email 2.
types:
Email:
type: object
properties:
name:
type: string
Emails:
type: array
items: Email
minItems: 1
uniqueItems: true
使用Email []相当于使用type:array。 items 切面定义了Email类型作为每个数组项继承的类型。
标量类型
RAML定义了一组内置标量类型,每个类型都有一组预定义的限制。
字符串
具有以下其他切面的JSON字符串:
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| pattern? | 此字符串应匹配的正则表达式。 |
| minLength? | 字符串的最小长度。值必须等于或大于0。<br /><br />Default: 0
|
| maxLength? | 字符串的最大长度。值必须等于或大于0。<br /><br />Default: 2147483647
|
例:
types:
Email:
type: string
minLength: 2
maxLength: 6
pattern: ^note\d+$
数字
任何JSON数字,包括带有以下其他方面的整型r:
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| minimum? | 参数的最小值。仅适用于类型号或整数的参数。 |
| maximum? | 参数的最大值。仅适用于类型号或整数的参数。 |
| format? | 值的格式。该值必须是以下之一:int32,int64,int,long,float,double,int16,int8 |
| multipleOf? | 如果使用此关键字的值除实例的结果为整数,则数值实例对“multipleOf”有效。 |
例:
types:
Weight:
type: number
minimum: 3
maximum: 5
format: int64
multipleOf: 4
整型
JSON数字的子集,是1的正数和负数的倍数。整数类型从数字类型继承其切面。
types:
Age:
type: integer
minimum: 3
maximum: 5
format: int8
multipleOf: 1
布尔
没有任何其他切面的JSON布尔值。
types:
IsMarried:
type: boolean
日期
必须支持以下日期类型表示:
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| date-only |
RFC3339的“全日期”符号,即yyyy-mm-dd。不支持时间或时区偏移符号。 |
| time-only | RFC3339的“部分时间”表示法,即hh:mm:ss [.ff ...]。不支持日期或时区偏移符号。 |
| datetime-only | 使用分隔符“T”组合仅日期和时间,即yyyy-mm-ddThh:mm:ss [.ff ...]。不支持时区偏移。 |
| datetime |
RFC3339; if format is set to rfc2616, uses the format defined in RFC2616.以下格式之一的时间戳:如果 format 被省略或设置为rfc3339,则使用 RFC3339的“date-time”符号;如果format设置为rfc2616,则使用RFC2616中定义的格式。 |
仅当类型等于datetime时,附加 format切面必须可用,并且值必须是rfc3339或rfc2616。任何其他值无效。
types:
birthday:
type: date-only # no implications about time or offset
example: 2015-05-23
lunchtime:
type: time-only # no implications about date or offset
example: 12:30:00
fireworks:
type: datetime-only # no implications about offset
example: 2015-07-04T21:00:00
created:
type: datetime
example: 2016-02-28T16:41:41.090Z
format: rfc3339 # the default, so no need to specify
If-Modified-Since:
type: datetime
example: Sun, 28 Feb 2016 16:41:41 GMT
format: rfc2616 # this time it's required, otherwise, the example format is invalid
文件
文件类型可以限制通过表单发送的内容。当这种类型在Web表单的上下文中使用时,它应该表示为以JSON格式的有效文件上传。文件内容应该是一个base64编码的字符串。
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| fileTypes? | 文件的有效内容类型字符串的列表。文件类型*/*必须是有效的值。 |
| minLength? | 指定参数值的最小字节数。该值必须等于或大于0。<br /><br />Default: 0
|
| maxLength? | 指定参数值的最大字节数。该值必须等于或大于0。<br /><br />Default: 2147483647
|
types:
userPicture:
type: file
fileTypes: ['image/jpeg', 'image/png']
maxLength: 307200
customFile:
type: file
fileTypes: ['*/*'] # any file type allowed
maxLength: 1048576
空类型
在RAML中,类型nil是一个标量类型,只允许nil个数据值。具体来说,在YAML中,它仅允许YAML的null(或其等价表示,例如〜),在JSON中它只允许JSON的null,在XML中它只允许XML的xsi:nil。在头部,URI参数和查询参数中,nil类型只允许字符串值nil(区分大小写);而具有字符串值“nil”(区分大小写)的实例,当用nil类型描述时,反序列化为nil值。
在下面的示例中,对象的类型,并有两个必需的属性,名称和注释,两者默认为类型字符串。例如,name被赋予一个字符串值,但是注释是nil,这是不允许的,因为RAML期望一个字符串。
types:
NilValue:
type: object
properties:
name:
comment:
example:
name: Fred
comment: # Providing no value here is not allowed.
下面的示例显示了nil类型赋值给`comment':
types:
NilValue:
type: object
properties:
name:
comment: nil
example:
name: Fred
comment: # Providing a value here is not allowed.
以下示例显示如何使用联合体表示nilable属性:
types:
NilValue:
type: object
properties:
name:
comment: nil | string # equivalent to ->
# comment: string?
example:
name: Fred
comment: # Providing a value or not providing a value here is allowed.
将属性的类型声明为nil表示类型实例中缺少值。在需要类型nil的值(仅仅是类型声明)的RAML上下文中,使用通常的YAML null,例如。当类型为nil|number时你可以使用枚举:[1,2,〜]或更明确/冗长enum: [ 1, 2, !!null "" ];在非内联表示法中,你可以完全忽略该值,当然。
联合体类型
联合类型用于允许数据的实例由几种类型中的任何一种来描述。联合类型通过组合由管道(|)符号分隔的2个或更多类型的类型表达式声明;这些组合类型被称为联合类型的超类型。在以下示例中,Device类型的实例可以由Phone类型或Notebook类型描述:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Phone:
type: object
properties:
manufacturer:
type: string
numberOfSIMCards:
type: number
kind: string
Notebook:
type: object
properties:
manufacturer:
type: string
numberOfUSBPorts:
type: number
kind: string
Device:
type: Phone | Notebook
当且仅当它满足与至少一个超类型相关联的所有限制时,联合类型的实例才有效。更一般地,当且仅当它是通过扩展该类型层次结构中的所有联合所获得的至少一个超类型的有效实例时,其类型层次结构中具有联合类型的类型的实例才有效。通过执行此扩展,然后将实例与所有超类型(从最左边开始并向右移动)进行匹配,来反序列化此类实例;第一个成功匹配的基本类型用于反序列化实例。
以下示例定义两种类型,第三种类型是这两种类型的联合。
types:
CatOrDog:
type: Cat | Dog # elements: Cat or Dog
Cat:
type: object
properties:
name: string
color: string
Dog:
type: object
properties:
name: string
fangs: string
以下CatOrDog类型实例的示例是有效的:
CatOrDog: # follows restrictions applied to the type 'Cat'
name: Musia,
color: brown
想象一下在多重继承类型表达式中使用的联合类型的更复杂的例子:
types:
HasHome:
type: object
properties:
homeAddress: string
Cat:
type: object
properties:
name: string
color: string
Dog:
type: object
properties:
name: string
fangs: string
HomeAnimal: [ HasHome , Dog | Cat ]
在这种情况下,类型HomeAnimal有两个超类型HasHome和一个匿名联合类型,由以下类型表达式定义:Dog | Cat。
验证HomeAnimal类型涉及验证从每个超类型派生的类型以及联合类型中每个元素的类型。在这种特殊情况下,处理器必须测试类型[HasHome,Dog]和[HasHome,Cat]是有效类型。
如果从两个联合类型扩展,处理器必须对每个可能的组合执行验证。例如,为了验证下面所示的HomeAnimal类型,处理器必须测试六种可能的组合:[HasHome, Dog ], [HasHome, Cat ], [HasHome, Parrot], [IsOnFarm, Dog ], [IsOnFarm, Cat ], and [IsOnFarm, Parrot]。
types:
HomeAnimal: [ HasHome | IsOnFarm , Dog | Cat | Parrot ]
使用XML和JSON模式
RAML允许使用XML和JSON模式通过将模式集成到其数据类型系统中来描述API请求或响应的主体。
以下示例显示如何将外部JSON模式包含在根级别类型定义和主体声明中。
types:
Person: !include person.json
/person:
get:
responses:
200:
body:
application/json:
type: !include person.json
RAML处理器不能允许定义XML或JSON模式的类型参与类型继承或特殊化,或者有效地在任何类型表达式中。因此,您不能定义这些类型的子类型以声明新属性,添加限制,设置切面或声明切面。但是,您可以创建添加注释,示例,显示名称或描述的简单类型封装。
以下示例显示有效的声明。
types:
Person:
type: !include person.json
description: this is a schema describing person
以下示例显示了继承JSON模式特征并添加其他属性的类型的无效声明。
types:
Person:
type: !include person.json
properties: # invalid
single: boolean
另一个无效的情况显示在下面的类型Person用作属性类型的示例中。
types:
Person:
type: !include person.json
description: this is a schema describing person
Board:
properties:
members: Person[] # invalid use of type expression '[]' and as a property type
RAML处理器必须能够解释和应用JSON模式和XML模式。
如果媒体类型分别不允许使用XML格式的数据或JSON格式的数据,则不得使用XML模式或JSON模式。 XML和JSON模式在查询参数,查询字符串,URI参数和标头的任何声明中也被禁止。
节点“模式”和“类型”以及“模式”和“类型”是相互排斥的,并且与RAML 0.8的兼容性是同义的。 API定义应使用“类型”和“类型”,因为“模式”和“模式”已弃用,可能会在将来的RAML版本中删除。
参考内部元素
有时需要引用模式中定义的元素。 RAML通过使用URL片段支持它,如下面的示例所示。
type: !include elements.xsd#Foo
当引用模式的内部元素时,RAML处理器务必对该特定元素验证实例。 RAML规范支持引用JSON模式中的任何内部元素,这些元素是有效模式,任何全局定义的元素和XML模式中的复杂类型。只有几个限制:
- 针对内部元素验证任何XML或JSON实例遵循与针对常规XML或JSON模式的验证相同的限制。
- 在XSD中引用复杂类型有助于确定XML实例的结构,但由于复杂类型未定义顶级XML元素的名称,因此这些类型不能用于序列化XML实例。
用户自定义切面
切面表示除了在其实例上施加的类型之外的各种附加限制,例如数字的可选的minimum和maximum切面,或者标量的enum切面。除了内置切面,RAML提供了一种方法来声明任何数据类型的用户定义切面。
在类型声明中使用可选facets切面声明用户定义切面。 facet切面t的值是一个映射。键命名用户定义的切面。相应的值定义了各个切面可以采用的具体值。属性声明和用户定义的切面声明的语法是相同的。切面根据切面面声明中定义的具体值限制子类型的实例,而不是其类型。
构面名称不得以开括号开头,以消除来自注释的名称。类型上的用户定义的构面名称不得与该类型的内置构面匹配,也不能与类型的继承链中的任何祖先类型的构面名称匹配。
如果类型的构面被声明为必需,则该类型的任何子类型必须为该构面定义一个值。
下面的示例定义了将日期限制为不在假日的日期的功能:
#%RAML 1.0
title: API with Types
types:
CustomDate:
type: date-only
facets:
onlyFutureDates?: boolean # optional in `PossibleMeetingDate`
noHolidays: boolean # required in `PossibleMeetingDate`
PossibleMeetingDate:
type: CustomDate
noHolidays: true
在本示例中,声明noHolidays 切面并将其值定义为布尔值,可以限制落在假日的日期实例。任何继承类型的实例(例如PossibleMeetingDate类型)必须具有不在假日的值。
根据定义,用户定义的facet不内置到此RAML规范中,因此它们的语义可能不被所有RAML处理器理解。因此,RAML处理器可以或可以不选择在验证该类型的实例时在类型上使用用户定义的facet。在上面的例子中,RAML处理器可以或不可以为noHolidays指定含义,因此可以选择在验证PossibleMeetingDate的实例时忽略noHolidays:true值。
确定默认类型
RAML处理器必须能够通过使用以下规则来确定类型声明的默认类型:
-
如果且仅当一个类型声明包含一个
properties切面,那么默认类型是object。以下代码段说明了此规则:types: Person: type: object properties:该规则也可以写成如下:
types: Person: # default type is `object`, no need to explicitly define it properties: -
如果且仅当类型声明既不包含
properties切面也不包含type或schema切面,那么默认类型是string。以下代码段说明了此规则:types: Person: properties: name: # no type or schema necessary since the default type is `string` -
默认类型
any应用于不包含properties,type或schema的任何body节点。例如:body: application/json: # default type is `any`
或者,如果已定义默认介质类型,则无需在此处声明:
body:
# default type is `any`
或者,如果已定义默认介质类型,则无需在此处声明:
types:
Person:
properties:
name:
type: number
类型表达式
类型表达式提供了一种强大的引用,甚至定义类型的方法。类型表达式可用于任何类型的预期。最简单的类型表达式只是类型的名称。使用类型表达式,您可以设计类型联合,数组,映射和其他东西。
| 表达式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Person |
最简单的类型表达式:单个类型 |
Person[] |
Person对象数组 |
string[] |
字符串标量数组 |
string[][] |
字符串标量的二维数组 |
| <code>string |Person</code> | 由字符串或 Person的成员组成的联合类型 |
| <code>(string | Person)[]</code> | 上面所示类型的数组 |
类型表达式可用于任何类型的预期位置:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Phone:
type: object
properties:
manufacturer:
type: string
numberOfSIMCards:
type: number
Notebook:
type: object
properties:
manufacturer:
type: string
numberOfUSBPorts:
type: number
Person:
type: object
properties:
devices: ( Phone | Notebook )[]
reports: Person[]
你甚至可以从一个类型表达式“扩展”。例如:
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
types:
Phone:
type: object
properties:
manufacturer:
type: string
numberOfSIMCards:
type: number
Notebook:
type: object
properties:
manufacturer:
type: string
numberOfUSBPorts:
type: number
Devices:
type: ( Phone | Notebook )[]
这个例子实际上声明了一个“类型别名”,它为使用复杂类型表达式定义的类型提供了一个更易读的名称(Devices)。在这种情况下,类型表达式由类型Phone和Notebook的联合数组组成。您可以使用此技术为复杂类型提供简单的名称。类型别名还可以包含额外的属性,例如描述和注释。
语法
类型表达式由内置或自定义类型和某些符号的名称组成,如下所示:
| 表达式组件 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 类型名称 | 类型名称,类型表达式的基本构建块,单独使用创建最简单的表达式。 |
number: 一个内置类型Person: 一个自定义类型 |
| (类型表达式) | 括号消除了的表达式的歧义。 | <code>Person | Animal[]</code> <code>(Person | Animal)[]</code> |
| (类型表达式)[] | 数组,一个一元的后缀操作符放在另一个类型表达式之后,根据需要括在括号中,表示结果类型是该类型表达式的实例数组。 |
string[]: 字符串数组Person[][]: Person数组实例的数组 |
| (类型表达式1) | (类型表达式2) | 中缀联合运算符指示生成的类型可能是类型表达式1或类型表达式2.多个联合运算符可以在类型表达式对之间组合。 | <code>string | number:</code> 一个字符串或者数字 <code>X | Y | Z</code>: X,Y,Z之一 <code>(Manager | Admin)[]:</code> 一个数组,其成员由Manager或Admin实例组成 <code>Manager[] | Admin[]:</code> 一个Manager实例数组或一个Admin实例数组。 |
多重继承
RAML类型支持多继承。这是通过传递一系列类型:
types:
Person:
type: object
properties:
name: string
Employee:
type: object
properties:
employeeNr: integer
Teacher:
type: [ Person, Employee ]
在上面的例子中,Teacher类型继承了Person和Employee的所有限制。
只有当子类型继承其父类型的所有限制后仍然是有效的类型声明时,才允许多继承。此外,不允许继承不同类型的原始类型,例如[number,string]。
在以下示例中,子类型Number3完全有效:
types:
Number1:
type: number
minimum: 4
Number2:
type: number
maximum: 10
Number3: [ Number1, Number2]
而使用相同的示例,只将类型Number2的最大值从10改为2将导致一个无效的类型Number3。
types:
Number1:
type: number
minimum: 4
Number2:
type: number
maximum: 2
Number3: [ Number1, Number2] # invalid, maximum value cannot be less than minimum value
联合类型章节说明了如何验证使用多个继承和联合类型的类型的另一个示例。
如果子类型从至少两个父类型继承具有相同名称的属性,则子类型保留应用于那些属性的所有限制,有两个例外:1)当父类型已声明“pattern“切面 2)用户定义的切面,当另一个用户定义的切面具有相同的值。在这些情况下,会发生无效的类型声明。
内联类型声明
您可以在任何可以引用类型的地方声明内联/匿名类型,除非在类型表达式中。
#%RAML 1.0
title: My API With Types
/users/{id}:
get:
responses:
200:
body:
application/json:
type: object
properties:
firstname:
type: string
lastname:
type: string
age:
type: number
在RAML中定义示例
高度推荐API文档包括丰富的选择范例。 RAML支持多个示例的定义或者一个类型声明的任何给定实例的单个。
多个示例
可选examples切面可用于将多个示例附加到类型声明。它的值是键值对的映射,其中每个键表示示例的唯一标识符,值是单个示例。
以下示例显示了examples切面的值:
message: # {key} - unique id
# example declaration
title: Attention needed
body: You have been added to group 274
record: # {key} - unique id
# example declaration
name: log item
comment: permission check
单个示例
可选example切面可用于将类型实例的示例附加到类型声明。有两种方法来表示示例facet值:作为特定类型实例的明确描述以及包含其他切面的映射。
作为特定类型实例的显式描述
例如:
title: Attention needed
body: You have been added to group 274
作为包含其他切面的映射
映射可以包含以下其他方面:
| 切面 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| displayName? | 示例的备用,人性化名称。如果示例是示例节点的一部分,则默认值是为此示例定义的唯一标识符。 |
| description? | 一个实质的,人性化的描述为例。它的值是一个字符串,可以使用markdown格式化。 |
| (<注释名>)? | 要应用于此API的注释 。注释是具有以“(”和“)”结尾的键的映射,其中括号中的文本是注释名称,值是该注释的实例。 |
| value | 类型实例的实际示例。 |
| strict? | 根据任何类型声明(默认)验证示例,或不验证。将此设置为false可避免验证。 |
例如:
(pii): true
strict: false
value:
title: Attention needed
body: You have been added to group 274
如何在RAML中定义example/examples中的示例
以下代码段说明了RAML API的不同级别的示例和示例属性的用法:
#%RAML 1.0
title: API with Examples
types:
User:
type: object
properties:
name: string
lastname: string
example:
name: Bob
lastname: Marley
Org:
type: object
properties:
name: string
address?: string
value?: string
/organization:
post:
headers:
UserID:
description: the identifier for the user who posts a new organization
type: string
example: SWED-123 # single scalar example
body:
application/json:
type: Org
example: # single request body example
value: # needs to be declared since instance contains a 'value' property
name: Doe Enterprise
value: Silver
get:
description: Returns an organization entity.
responses:
201:
body:
application/json:
type: Org
examples:
acme:
name: Acme
softwareCorp:
value: # validate against the available facets for the map value of an example
name: Software Corp
address: 35 Central Street
value: Gold # validate against an instance of the `value` property
类型实例的XML序列化
为了促进对XML序列化的潜在复杂过程,RAML为类型声明引入了一个附加的xml节点。此节点用于配置类型实例应如何序列化为XML。 xml节点的值是包含以下节点的映射:
| 名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| attribute? | boolean |
true 将类型实例序列化为XML属性。只可以对标量类型使用true。默认: false
|
| wrapped? | boolean |
true 在自己的XML元素中封装类型实例。 标量类型或者同一时刻attribute为true的时候都不能为true。 默认: false
|
| name? | string |
覆盖XML元素或XML属性的名称。 默认: 类型或属性的名称 |
| namespace? | string |
配置XML命名空间的名称。 |
| prefix? | string |
配置在序列化到XML期间使用的前缀。 |
以下类型声明显示了使用xml节点的示例:
types:
Person:
properties:
name:
type: string
xml:
attribute: true # serialize it as an XML attribute
name: "fullname" # attribute should be called fullname
addresses:
type: Address[]
xml:
wrapped: true # serialize it into its own <addresses>...</addresses> XML element
Address:
properties:
street: string
city: string
上面的示例可以序列化为以下XML:
<Person fullname="John Doe">
<addresses>
<Address>…</Address>
...
</addresses>
</Person>
在RAML中使用类型
类型可以在几个位置使用:
- Body ( JSON )
- Body ( XML )
- Body ( Web Form )
- Headers
- Query Parameters
- URI Parameters
关于序列化的要点是:
- 序列化规则取决于类型和使用类型的位置。
- “string”是自定义值类型的默认序列化目标,它是内置类型的扩展“值”。
- 扩展内置类型继承其序列化目标。


